Kubernetes Node
Contents
- Kubernetes is an open-source container orchestration tool developed by Google.
- It helps us manage containerized applications in different deployment environments.
Container Orchestration
- The automated deployment and management of containers is called container orchestration.
- Containers act as perfect hosts for micro-services (running independently).
- The rise of micro-services architecture led to applications using 1000s of containers that need to be smartly managed.
- Container orchestration offers:
- High Availability (no downtime)
- Horizontal Scalability
- Disaster Recovery
- And so much more..
Kubernetes Node
- A physical or virtual machine on which Kubernetes is installed.
- Nodes are cluster scoped. They are not scoped within a namespace.
- When you install Kubernetes on a node, the following components are installed. Some of them are used in worker nodes and the rest are used in master nodes.
- Kube API Server
etcdService- Kubelet Service
- Container Runtime (Docker Engine, CRI-O, containerd)
- Kube Controller
- Kube Scheduler
- A cluster is a collection of nodes grouped together
Worker Nodes
- These nodes do the actual work so they need to have more resources.
- Each worker node can have multiple pods running on it.
- 3 processes must be installed on every worker node.
- Container Runtime (eg. Docker Engine, CRI-O, containerd)
- Kubelet
- process of Kubernetes
- starts pods and runs containers inside them
- allocates resources from the node to the container
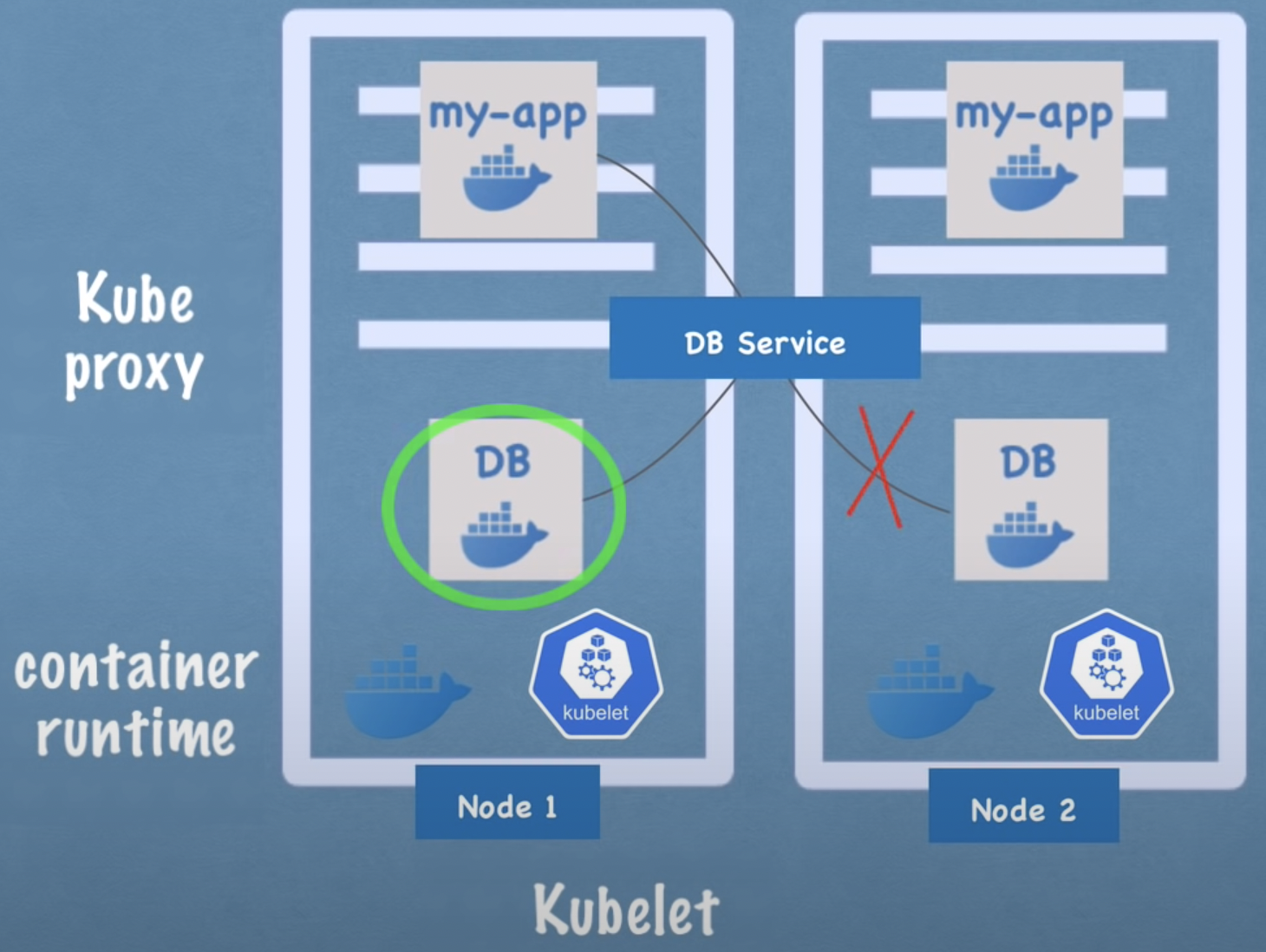
- Kubeproxy
- process of Kubernetes
- forwards the requests to pods intelligently
- Example: Kubeproxy forwards requests to the DB pod running on the same node to minimize network overhead.
Master Nodes
- Control the cluster state & manage worker nodes
- Need less resources as they typically only run core components of kubernetes
- Multi-master setup is often used for fault tolerance
- 4 processes run on every master node
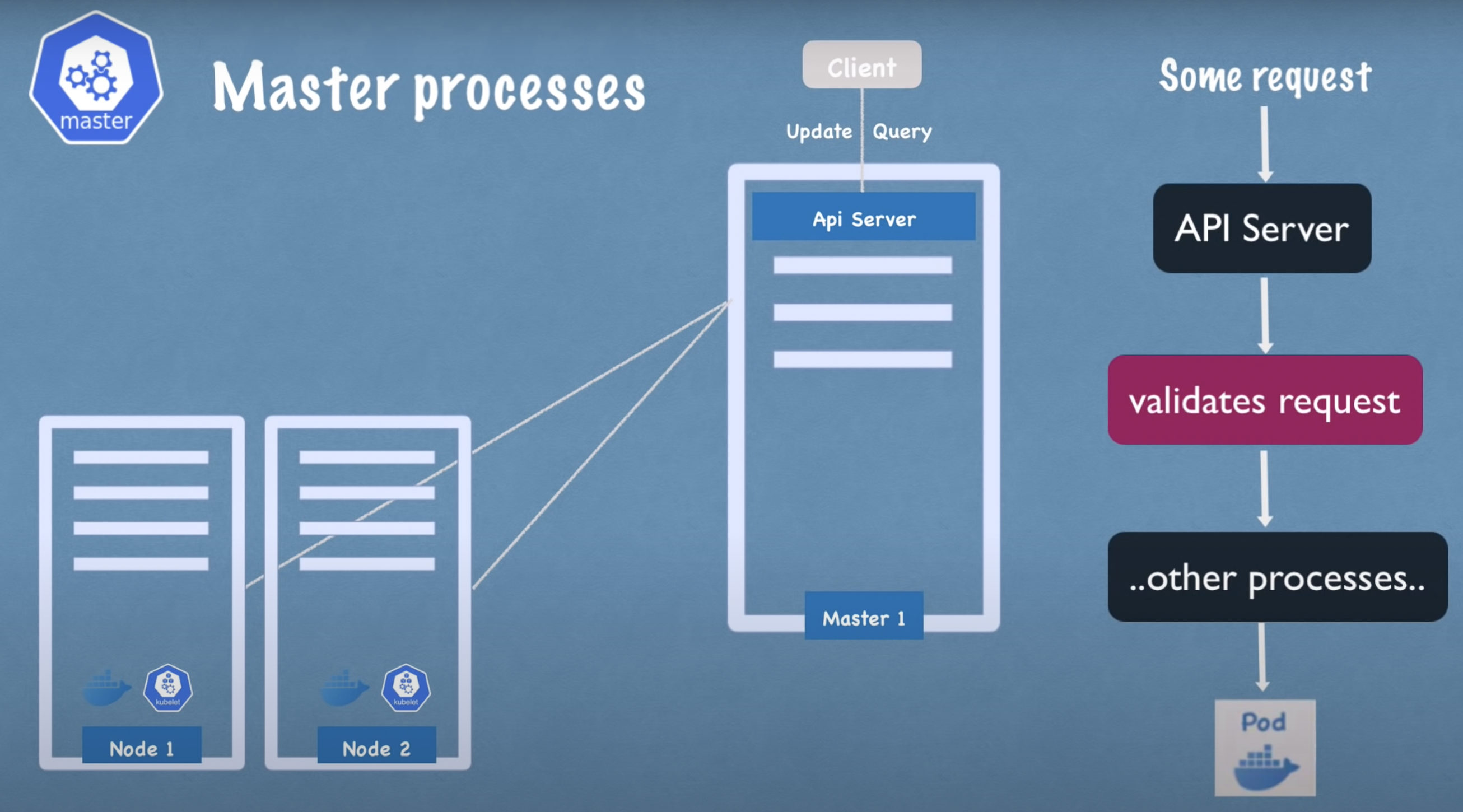
Kube API Server
- User interacts with the cluster via the Kube API server using a client (Kubernetes Dashboard, CLI, or Kubernetes API)
- Cluster gateway (acts as the entry point into the cluster)
- Can be used for authentication
Kube Scheduler
- Decides the node where the new pod should be scheduled and sends a request to the Kubelet to start a pod.
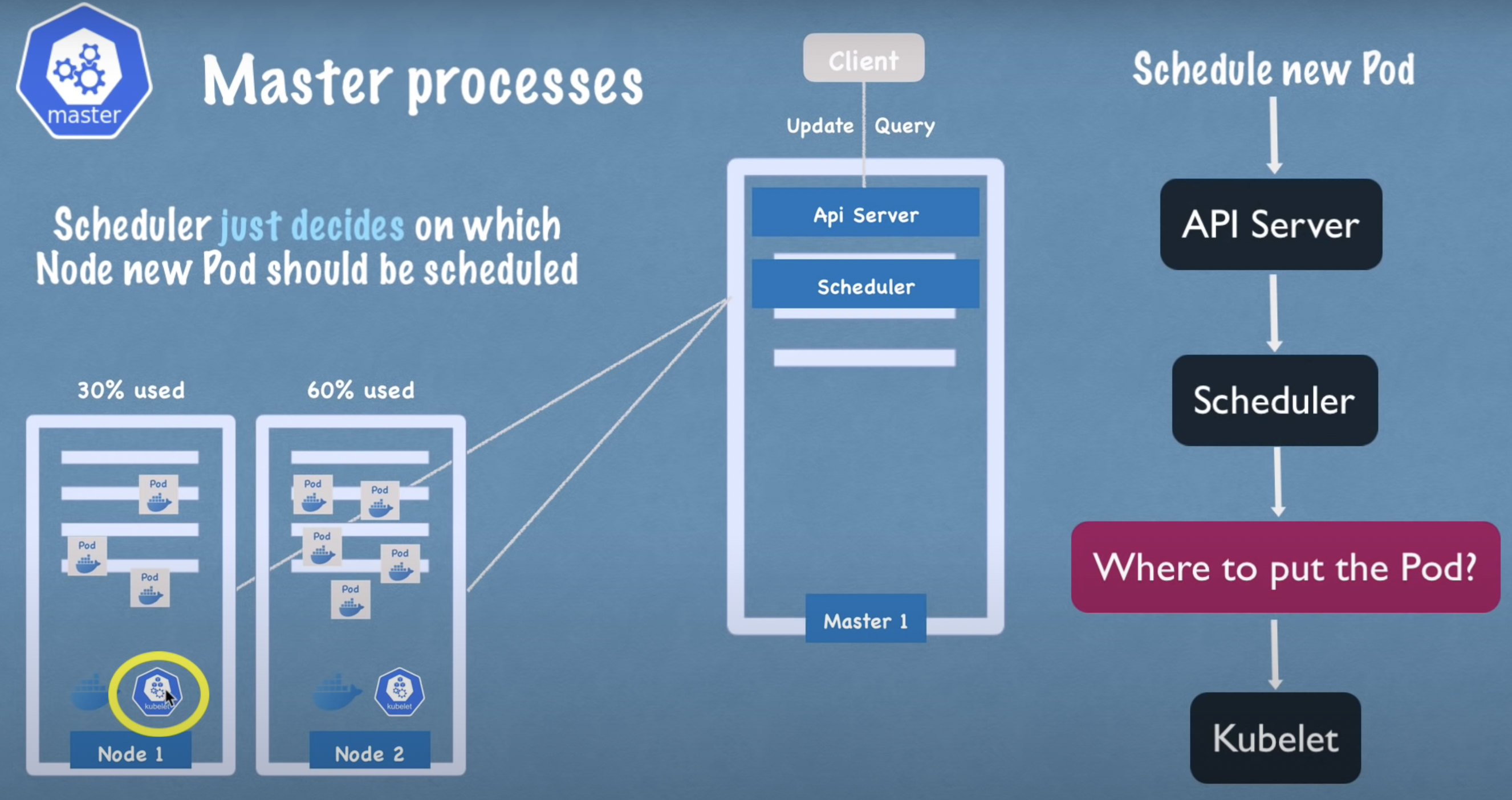
- Decides the node where the new pod should be scheduled and sends a request to the Kubelet to start a pod.
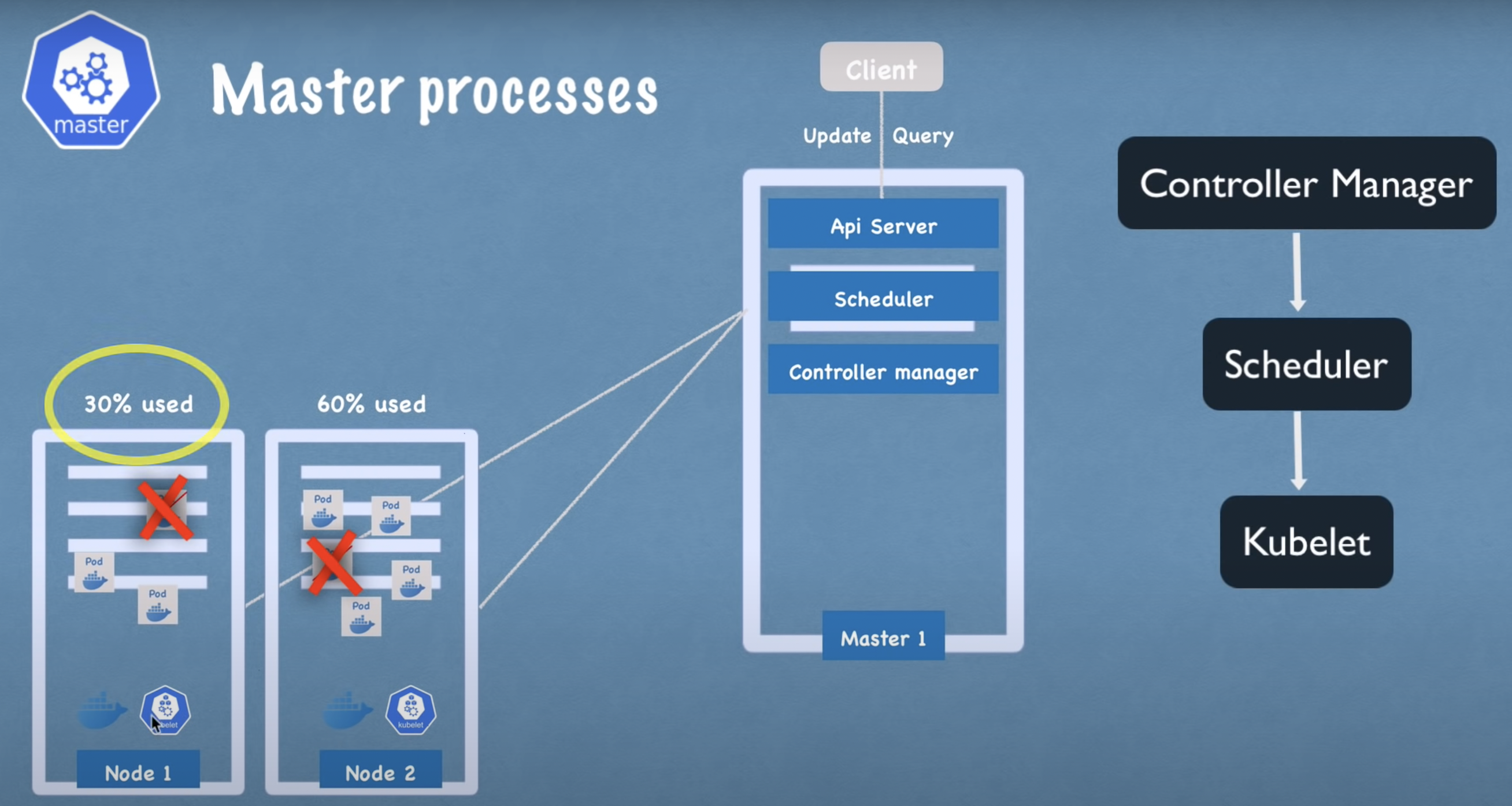
Kube Controller
- Detects state changes like crashing of pods
- If a pod dies, it requests scheduler to schedule starting up of a new pod
etcd
- Key-value store of the cluster state (also known as cluster brain)
- Cluster changes get stored in the etcd
- In multi-master configuration, etcd is a distributed key-value store
- Application data is not stored in the etcd